Deuterium Depleted Water
Deuterium depleted water is water that has it's levels of deuterium in the water decreased to lower levels. This is to help with the reduction of oxidative stress in the biology of mammals.
What is Deuterium?
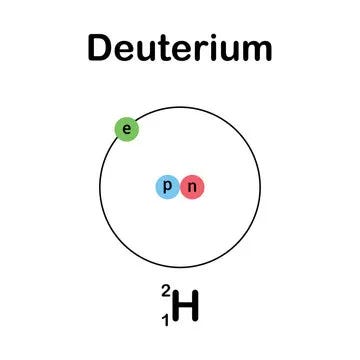
Deuterium (symbol: ²H or D) is a stable isotope of hydrogen. It is sometimes called heavy hydrogen because it has a neutron in its nucleus, in addition to the single proton found in regular hydrogen (protium, ¹H). This makes deuterium twice as heavy as regular hydrogen.
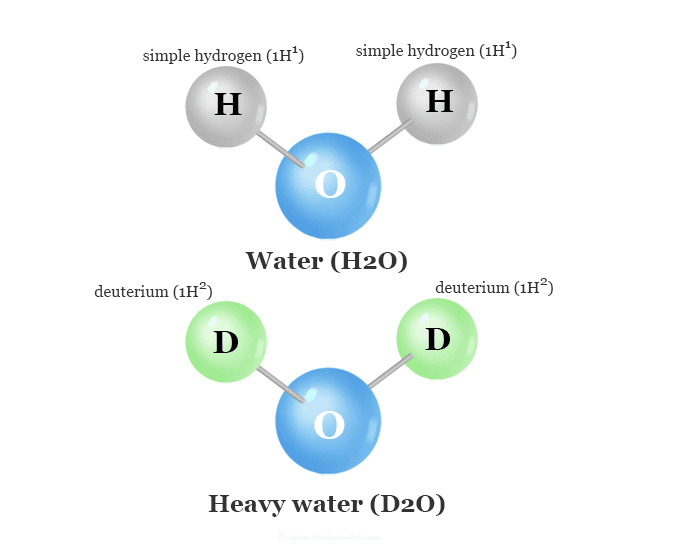
Water we normally think of as H2O in this case of heavy water it D2O where the Hydrogen atoms are replaced with Deuterium which is thought of as Hydrogen (proton) with a neutron. This changes the chemical reaction times and properties of the heavy water which affects the biological function of the cells in our biology.
Image: https://www.priyamstudycentre.com/2022/06/heavy-water.html
Image: Copilot
Key Properties of Deuterium
Atomic Structure:
Protium (¹H): 1 proton, 0 neutrons.
Deuterium (²H): 1 proton, 1 neutron.
Tritium (³H): 1 proton, 2 neutrons (radioactive).
Natural Abundance:
Deuterium occurs naturally at a concentration of approximately 0.0156% (156 ppm) in Earth’s water.
Atomic Mass: About 2 atomic mass units (amu), compared to 1 amu for protium.
Chemical Symbol: Often written as D or ²H (the latter emphasizes its isotope nature).
Physical Properties:
Deuterium-containing compounds, such as deuterium oxide (D₂O) or "heavy water," have slightly different physical properties than their protium counterparts. For example:
D₂O has a higher boiling point (101.4°C) than H₂O (100°C).
D₂O is about 10% denser than H₂O.
Uses of Deuterium
Nuclear Applications:Heavy Water Reactors: D₂O is used as a moderator in certain nuclear reactors (e.g., CANDU reactors) to slow down neutrons for sustaining nuclear fission.
Fusion Research: Deuterium is used in nuclear fusion experiments (e.g., deuterium-tritium fusion).
Scientific Research:
Tracer Studies: Deuterium is used as a tracer in chemical and biological experiments to study reaction pathways and metabolic processes.
Spectroscopy: Deuterium is used in NMR spectroscopy and mass spectrometry to analyze molecular structures.
Pharmaceuticals:
Some drugs incorporate deuterium instead of hydrogen to slow metabolism and improve drug stability.
Energy Production:
Deuterium is a potential fuel for fusion power, a future source of clean energy.
Industrial and Environmental:
Deuterium is used in manufacturing processes for semiconductors, optics, and isotopic labeling.
Heavy Water (D₂O) vs. Normal Water (H₂O)
Heavy Water (D₂O): Water in which both hydrogen atoms are deuterium.
Used in nuclear reactors.
Not toxic in small amounts, but large quantities can disrupt biological processes due to differences in chemical kinetics.
Deuterium-Depleted Water (DDW): Water with less deuterium than naturally occurring water.
Used in health and medical research.
Deuterium in Fusion Energy
In fusion reactions, deuterium can combine with:
Another deuterium nucleus (D + D reaction), producing tritium or helium-3.
Tritium (D + T reaction), producing helium-4 and a neutron, releasing massive amounts of energy.
Deuterium is abundant in seawater, with about 33 grams per ton of water, making it a potentially limitless fuel source for fusion energy.
Deuterium Depleted Water
Deuterium-depleted water (DDW), also known as light water, is water with a lower concentration of deuterium (a stable isotope of hydrogen) than naturally occurring water. Regular water contains about 150 parts per million (ppm) of deuterium. DDW typically has deuterium concentrations reduced to 125 ppm or lower, depending on the production process.
How DDW is Produced
Deuterium is separated from water through processes like:
Distillation: Repeated heating and cooling to remove heavier isotopes.
Electrolysis: Using electrical currents to separate hydrogen isotopes.
Fractional Crystallization: Exploiting differences in freezing points of isotopes.
Claimed Benefits of DDW
While research is ongoing, proponents of DDW suggest potential health benefits:
Cancer Therapy: Some studies suggest that reduced deuterium levels may slow cancer cell proliferation.
Cellular Metabolism: It may enhance mitochondrial efficiency, potentially improving energy production.
Anti-aging: DDW is believed to slow aging processes by reducing oxidative stress and DNA damage.
Improved Hydration: Some claim it hydrates cells more effectively than regular water.
Scientific Evidence
- Limited clinical studies (mainly in animals and small human trials) have shown that reducing deuterium levels might impact metabolic and cellular functions.
- However, the evidence is not yet conclusive, and DDW is not officially approved for treating or preventing diseases.
Risks and Considerations
- Cost: DDW can be expensive due to the complex production process.
- Insufficient Evidence: While it is generally safe, claims about its benefits often lack robust scientific validation.
Uses
- Research: Used in studies of cellular processes and isotopic effects.
- Dietary Supplement: Marketed as a health supplement in some countries.
Would you like more specific details, such as the science behind its health claims or its role in particular applications?
Deuterium Depleted Water Benefits
This is for informational purposes only. For medical advice or diagnosis, consult a professional.
Deuterium-depleted water (DDW) has been studied for potential health benefits, but the scientific evidence is still limited and ongoing. Some of the potential benefits that have been suggested in research include:
Anti-aging: Some studies suggest DDW may slow down aging processes by affecting cellular metabolism.
Cancer treatment: Research explores its potential role in cancer therapy, such as inhibiting tumor growth and improving the effectiveness of certain treatments.1
Neurodegenerative diseases: Preliminary studies suggest possible benefits for conditions like Alzheimer's and Parkinson's.
Important Notes:
Limited scientific evidence: The claims about the health benefits of DDW are largely based on preliminary research.
Safety: The long-term safety of consuming DDW is not fully established.
Availability and Cost: DDW is currently expensive and not widely available.
Disclaimer:
This information is for general knowledge and does not constitute medical advice.
Consult with a healthcare professional before making any decisions related to your health or considering the use of DDW.
It's crucial to note that the scientific understanding of DDW and its potential benefits is still evolving. More research is needed to fully understand its effects on the human body.
How to make Deuterium Depleted Water at Home?
Making deuterium-depleted water (DDW) at home is technically challenging and requires specialized equipment. However, it can theoretically be achieved using processes like fractional freezing or distillation, which exploit the physical differences between regular water and deuterium-rich water. Below is an outline of how these methods could work on a small scale:
1. Fractional Freezing Method
Deuterium-rich water freezes at a slightly higher temperature than regular water. By carefully controlling freezing, you can reduce deuterium levels.
Steps:
1. Prepare Regular Water: Use distilled water as a starting point to minimize impurities.
2. Partially Freeze: Place the water in a freezer and cool it slowly. The first ice crystals that form will be slightly richer in deuterium.
3. Remove the Ice: Discard the initial layer of ice, as it contains more deuterium.
4. Repeat: Refreeze the remaining liquid multiple times to progressively reduce deuterium content. Each cycle lowers the concentration of deuterium.
Challenges:
- This process is inefficient, as the reduction in deuterium concentration per cycle is minimal.
- It requires careful temperature control and is time-consuming.
2. Distillation Method
Deuterium-rich water boils at a slightly higher temperature (101.4°C compared to 100°C for regular water). By distilling water and collecting the lighter vapor, you can reduce deuterium content.
Steps:
1. Set Up a Distillation System:
- Use a home distiller or set up a distillation apparatus with a heat source, a condenser, and a collection vessel.
2. Boil Water:
- Heat water gently and collect the vapor (steam).
- Avoid collecting the first and last portions of the distillate, as deuterium concentrates in these fractions.
3. Repeat the Process:
- Redistill the collected water multiple times to progressively reduce deuterium concentration.
Challenges:
- Requires precise temperature control to separate deuterium effectively.
- Repeated distillation is necessary, which consumes time and energy.
Why It’s Difficult to Achieve at Home
- The difference in boiling and freezing points between deuterium-rich water and regular water is very small (fractions of a degree), requiring precision equipment.
- Industrial production involves sophisticated methods like vacuum distillation and electrolysis, which are difficult to replicate at home.
Practical Consideration
For most people, making DDW at home is not feasible without significant effort and equipment. If you're interested in consuming DDW for health purposes, purchasing it from reputable suppliers is a more practical option.
Additional ways to treat water
It's been reported that water that comes from nature that has had the natural process of structuring water is also low in deuterium.
Water that has flowed over rocks and formed vortexes or swirling pools in water is a process of structuring water that occurs naturally. Viktor Schauberger has done numerous studies on the effects of streams on water and how it naturally produces structured water.
Ways to structure water:
Swirl or stir your water into a vortex. The longer you do this the more effective it is.
Start with distilled water or de-ionized water
There are machines you can buy online that will do this mechanically to aid in the process of structuring the water. Such as the Mayo machine.
Crystals brought near or in your water will help structure the water. Crystals (in stones) help to structure the water.
Putting sea salt in your water help as the crystals of the salt and minerals help structure the water.
Putting fruit such as lemons, cucumbers, tea leaves, mint leaves, matcha tea, moringa powder in your water helps structure the water.
Putting your water in a clear glass jar (must be glass) and putting it in the sun helps structure the water. This is an important part to help in the structuring part.
Magnets near your water can help structure your water. Running the water through hoses wrapped around magnets (strong) helps in structuring the water.
Videos:
What is Deuterium-Depleted water (DDW)?
How to Make Deuterium Depleted Water DDW
9 Tips How to Drink the Healthiest Water | Dr. J9 Live
Papers:
Revealing water's secrets: deuterium depleted water
https://bmcchem.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/1752-153X-7-103
Sources
ChatGPT
Gemini 1.5 Flash
Viktor Schauberger - The Water Wizard – The Extraordinary Properties of Natural Water
Gerald H. Pollack - The Fourth Phase of Water